yarn
Yet Another Resource Negotiator Lets first go through how things are in hadoop initial version and what the limitations are which is solved by YARN.
processing in hadoop / mr version 1
in hdfs storage metadata is stored in name node and actual data blocks in data node. job execution is controlled by job tracker(running on master) and task tracker (on slave)
job tracker
a lot of work is done in terms of-
scheduling:
- deciding which job to execute first based on scheduling logic
- priority of jobs
- checking available resources
- allocating resources to jobs
monitoring:
- tracking the progress of job
- rerun task to recover from failure
- for slow task start on other node
task tracker
tracks tasks on each data node and informs the job tracker
limitations of hadoop / mr version 1
scalability: when cluster size goes beyond 4k data nodes then the job tracker used to become a bottleneck
resource utilization: need to configure fixed number of map and reduce slots at the time of cluster setup. if a job requires more map slots to be used then its problem
job support: only map reduce jobs were supported
solution
major bottleneck was that job tracker was doing a lot of work in scheduling and monitoring. yarn solved these problems.
it has three components:
resource manager
- monitoring aspect is taken away from job tracker and in yarn its scalled as resource manager
- only does scheduling
- the resource manager creates a container(cpu + memory) on one of the node manager(task tracker), inside this container the resource manager creates an application master
- allocates the resources in the form of containers and details(containerid, hostname) will be send to application master
node manager
same as task tracker
application master
- take care of end to end monitoring for the application
- asks the resource manager for resources
- requests for resources in the form of number of containers(cpu + memory)
limitations of hadoop / mr version 1 (solved)
scalability: monitoring is offloaded to application master so for different applications, will have different application master to monitor
resource utilization: no more fixed map reduce slots, with the logical containers the resource allocation is much more dynamic and we can request for any amount of cpu or memory with this the cluster utilization is improved.
job support: can run spark, tez etc
uberization
if job is very small that can be solved inside application master itself then application master will not ask for more resources and run within, this mode is uberization.
yarn architecture
ways to execute spark jobs
- interactive mode via spark-shell/pyspark/notebooks
- as a job by spark-submit
cluster manager
controls cluster and allocates driver and executor, different cluster managers are:
- yarn
- k8s
- mesos
here we will be looking in yarn only
how program is executed on cluster
- master/slave architecture
- driver analyses work, divides in many tasks, distributes tasks, schedules task and monitor
- executor is jvm process which has some cpu and memory, exeute code
As shown below, when client submits spark job(spark-submit) then driver and executors are launched in cluster, for each job different driver and executors will be launched.
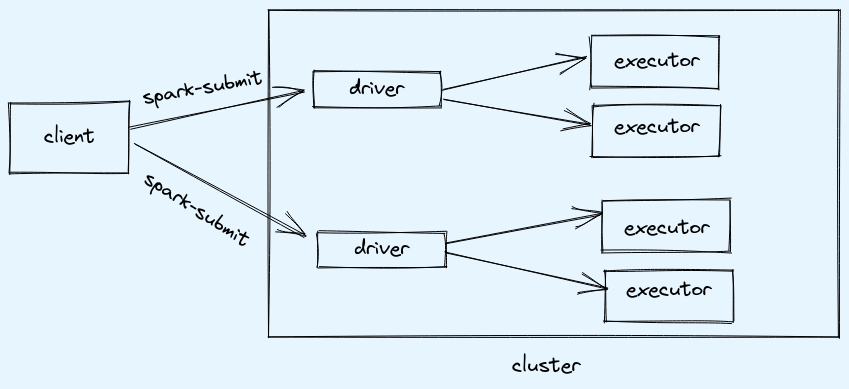
Note:
- executors always launched on cluster (worker nodes)
- driver can run on client or cluster
client mode: when driver runs on client machine
- launch spark-shell creates spark session
- once spark session created request goes to resource manager
- resource manager then will create a container on one of the node manager and will launch application master for the submitted spark application
- application master will then negotiate resources from resource manager in form of containers
- resource manager will then create containers in the node managers
- application master will then create executors in those containers
- driver and executors can now communicate directly
cluster mode: when driver runs on cluster
it is similar to client mode with difference, driver will be running on application master and will negotiate with resource manager for resources
local mode: single jvm process with driver and executor used for local testing
Note: spark session is like data structures where driver maintains all information including location, status etc.

Comments