hive basics
it is open source datawarehouse to process structured data on top of hadoop
why hive
writing map reduce code to process data on hadoop requires lot of code, to cater this problem hive was developed which is sql like query known as hive ql, internally hive produces map reduce and run it on hadoop cluster
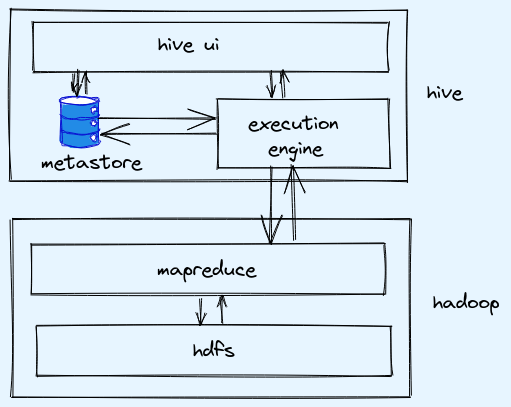
architecture
-
actual data: stored in hdfs as files
-
metadata: stored in database as hdfs is for write once and read only, hdfs does not support modification for schema evolution and hdfs will also have high latency compared to database thats why database is used for metadata
- hive is schema on read, no constraints
- minimal index support
- only equi-joins
- restricted sub queries
metastore
- stores metadata of all hive tables
- map files and directories in hdfs to tables
- holds table schema
- any database with jdbc driver can be used as metastore
- when query is done in hive then schema from metastore is imposed on the data to get tabular view
- default is
derbydatabase, not recommended as it allows only one connection at a time
In clodera quickstart mysql is used for metadata, database name is metastore and we can connect to that database to query what metadata is stored. For example TBLS tables has details of the hive tables
data storage details
- by default data is stored in warehouse directory
/user/hive/warehouse - creating new database
dbname, location will be/user/hive/warehouse/dbname.db - creating new table
abcin databasedbname, location will be/user/hive/warehouse/dbname.db/abc, which will have mutiple files depnending on data - default location can be change by setting property
hive.metastore.warehouse.dirin filehive-site.xml - tables created in default will be directly in
/user/hive/warehouse
complex data types
array
- same data types in an array
- no fixed size
create table table1 (
id int
col1 array<string>
);
insert into table1
select 1, array("value1", "value2");
--output: 1 value1
select id, col1[0] from table1;
/*
if we have more columns in table and we load data from file which has less columns
then also load will happen it wont fail, additional columns in table will get null values
*/
map
- key, vaule pair
- keys should be distinct
- value can be accessed using key
- key and value can have different data types
- unordered, order does not matter
- each key, value pair is called an entity
create table table1 (
col1 int,
col2 array<string>,
col3 map<string, boolean>
)
row format delimited
field terminated by ','
collection items terminated by '#'
map keys terminated by ':';
struct
- its like a class
- logical group of data
- can have different data types
- can hod any number of values
- value refrenced by name
create table table1 (
col1 int,
col2 array<string>,
col3 struct<s1:string, s2:string>
);
select col1, col3.s1 from table1;
built in functions
UDF (User Defined Functions)
- system functions
- works on single row and output single row
- example: concat(), round(), length()
UDAF (User Defined Aggeregate Functions)
- works on multiple rows and output single row
- example: sum(), avg()
UDTF (User Defined Tablegenerating Functions)
- works on single row and output multiple rows
- example: explode(), posexplode()
--
create table table1(co11 string, col2 array<string>)
row format delimited
fields terminated by ','
collection items terminated by ":";
load data local inpath '/path/to/file'
into table table1;
/*
--output:
name1 ["a", "b", "c"]
name2 ["d", "e", "f"]
.
.
*/
select * from table1;
/*
--output:
a
b
c
d
e
f
.
.
*/
select explode(col2) from table1;
--with explode we only get exploded column not other columns for selecting other columns we need to use lateral view
lateral view
virtual table formed by exploded view, which can be joined with original table to allow complex query
select col1, exploded_col from table1
lateral view explode(col2) exploded_data as exploded_col;
custom functions (UDF)
in case in built functions can not solve the requirement then we can write custom functions in hive using java
example: lets say we want to make function which can do uppercase of string
- write java code for making input to uppercase
- bundle code in jar file
- add jar and create temporary function
package example;
import org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.UDF;
public class ExampleClass extends UDF {
public String evaluate(String input){
if(input==null)
{
return null;
}
return (input.toString().toUpperCase());
}
}
ADD JAR /pat/to/jar/example.jar;
create temporary function ucase as'example.ExampleClass';
create table table1 (
col1 string
);
insert into table1
select 'val1'
select ucase(col1) from table1;
Note: Some external jars might be required like hive-exec-1.2.2.jar
This temporary function will be available only in the connected hive session not globally. For solving this problem we need to add jar in hdfs and create permanent function.
hadoop fs -put example.jar /path/to/hdfs/
CREATE FUNCTION ucase AS
'example.ExampleClass' using JAR
'hdfs://localhost:8020/path/to/hdfs/example.jar';
set operations
union
- supported in hive
- union removes duplicates
- union all preserves duplicates
minus
not supported in hive
intersect
not supported in hive
sub queries
from clause
select * from (
select id from table1
union all
select if from table2
) t;
where clause
supports only two types:
in/not in:
- subquery should be for single column
- subquery should return list of column values
- subquery should not reference parent query
select id from table1
where table1.id in (
select id from table2
);
exists/not exists:
- subquery should reference parent query
select id from table1
where exists (
select id from table2 where table2.id=table1.id
);
views
- virtual table with subset of data from a larger table
- stored as query in hive metastore
create view view1
as
select col1, col2
from table1
- restrict access to data
- create different logical tables from base table
basic commands
--this will give all the databases in hive
show databases;
--to create new database
create database abc;
--to change database
use abc;
--to create new table
create table new (
id int,
name string
);
--to show tables
show tables;
--to show schema of table
describe new;
--to show extended details of table like location, type, etc.
describe formatted new;
--to insert in table, it will run map reduce job
insert into new values
(1, "abc");
--to insert mutiple rows
insert into new values
(1, "A"),(2, "B");
to check files in the hdfs where hive tables are stored
hadoop fs -ls /user/hive/warehouse/new.db/abc
to check content of file in the hdfs where hive tables are stored
hadoop fs -cat /user/hive/warehouse/new.db/abc/*
connecting to hive
hive prompt: directly in shell launch hive and query
hue: hadoop user experience, its UI to query hive, spark, etc.
beeline: gives better view and secure
beeline -u jdbc:hive2://
#to execute query from terminal
beeline -u jdbc:hive2:// -e "select * from new.abc"
#to execute file with hive queries from terminal
beeline -u jdbc:hive2:// -f /path/to/file.hql
--to quit from beeline
!q
--to execute file from beeline
source /path/to/file.hql
types of table
managed
- hive manages the table, have control of data(files & directories)
- if table is dropped both data and metadata will be deleted
- by default table created is managed
- table type can be checked in
describe formatted table_name;
external
- hive manages only metadata
- if tables is dropped only metadata is deleted
- if data is used by other apps like spark then we should be using external tables
create external table prod(
id int,
name string
)
location 'path/to/data';
Note: In hive command prompt if we need to query file we can use dfs
example: dfs -ls /path/to/file
load data in hive
insert command
not recommended takes lot of time, doing inserts may create some tmp tables which will be there until session is alive.
load from file
from local to hive table
create table if not exists table1(
id int,
name string
)
row format delimited
fields terminated by ','
stored as textfile;
--to load data in the table
load data local inpath
'/local/path/to/file'
into table table1;
here table will be managed as its default type and data path will also be in default location. It will be copied over from local to hdfs.
from hdfs to hive table
hadoop fs -copyFromLocal /local/path/to/file /path/on/hdfs
--to load data in the table
load data inpath
'/path/on/hdfs'
into table table1;
--to overwrite
load data inpath
'/path/on/hdfs'
overwrite into table table1;
here it will be cut paste instead of copy
table to table
create table if not exists table2(
id int,
name string
)
row format delimited
fields terminated by ','
stored as textfile;
insert into table table2
select * from table1;

Comments