hdfs architecture
hdfs is hadoop distributed file system. Highly fault tolerant and is designed to deploy on low cost machines.
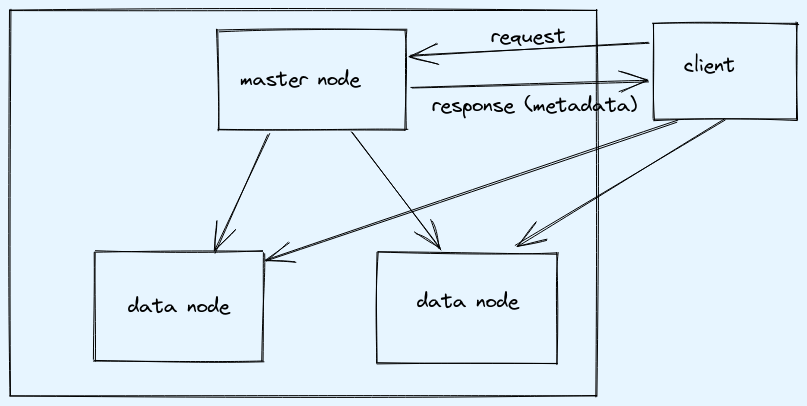
Let’s assume we have cluster(2 data node, 1 name node) and file of 250MB.
- Default block size: 128MB
- Default replication factor: 3
So, there will be 2 blocks:
- Block-1: 128MB
- Block-2: 122MB
When data will be loaded then both the blocks will be loaded on different data node, behind the scene as per default setting each block will be replicated 3 times, in this case 1 node will have 2 copies of block and other node will have 1 copy of block.
Note:
- last block might have less than 128MB depending on the size of file, but space is not wasted as remaining space will free up and is used by other blocks.
- one data block cannot be shared by two files, so last block of one file is not used by other file bock
Metadata stored in name node
At high level below details are stored in metadata.
- Filename
- Block
- Data node: All the data nodes which have the block
Example:
| File name | Block Number | Data node 1 | Data Node 2 | Data Node 3 |
Data node failure
In case of any failue in data node other data node will be responsible for serving requests and name node will maintain the copies as per replication factor.
1. Dead data node
Each data node sends heart beat every 3 seconds to name node and if 10 consecutive times hear beat is not received from a data node then data node is treated as dead or running very slow.
2. Corrupt data node
Each data node sends block report using which name node can identify if block is corrupted then will replicate the block from known good replica and mark the corrupted one for delete.
Name node failure
In case of failure of name node there will be no access to metadata. So in hadoop v1 it was single point of failure. In hadoop v2 it has secondary name node so it’s not single point of failure. Important metadata files:
- fsimage: snapshot of file system at a particular time
- edit logs: transaction logs that changes in hdfs file system
Secondary name node is responsible for merging fsimage with edit logs and generating new fsimage, once merge is done it restes fsimage and edit logs to empty. This process is done every 30 sec.
So, when primary name node fails, secondary can become active and then we have to introduce secondary name node.
Block size
In hadoop v2 default block size is 128MB, if it is increased then we might have less blocks to process then nodes so cluster might be under utilized, if block size is decreased then we might have a lot of blocks which will increse burden on name node to keep track of metadata and handling it.
Hadoop HA
High availibility is achieved by two name nodes primary and hot standby. If primary goes down then standby takes overs. It can be achieved using quorum journal manager.
Three journal nodes are used and metadata is copied over from active name node and here secondary is called as standby name node and still does the same checkpointing work to combine fsimage snaphot with edit log reading from journal nodes. Standby keeps lock on jk(zookeeper) and always check if its locked or not, if not then takes lock and becomes active.
Note: Three journal nodes are used to tolerate single machine failure. The system can tolerate at most (N-1) / 2 failures when running with N JournalNodes.

Comments