MapReduce working
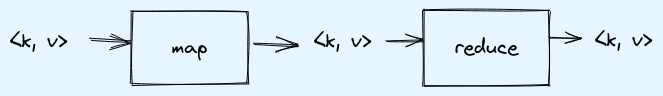
MapReduce is programming model for processing big datsets. It consists of two stages:
- map
- reduce
Both works on key value pairs.
| key | value |
| id | 1 |
| name | abc |
Understanding with example
Lets say we have a big file (size 100GB) and we need to find frequency of words. By default block size is 128MB so data will be divided as per block size and distributed among nodes. Considering with default one reducer.
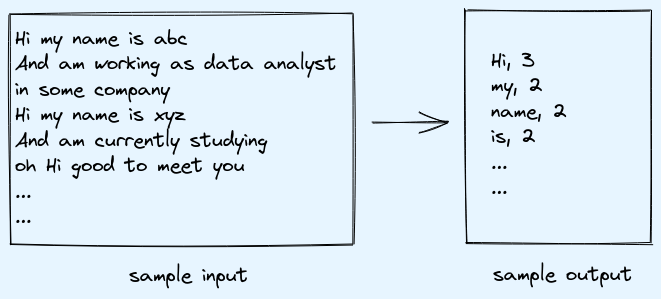
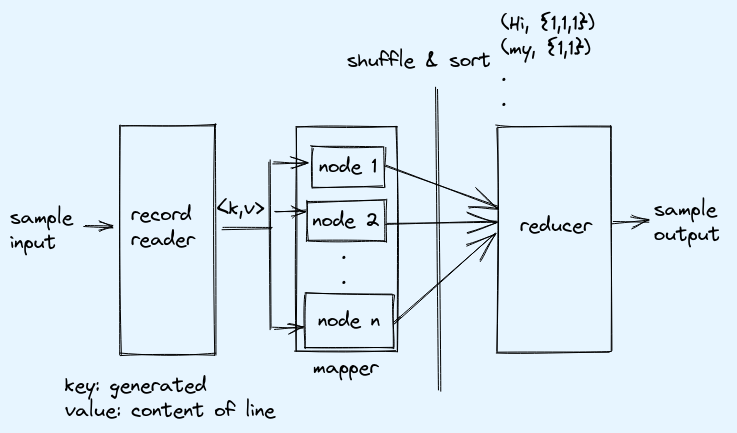
Clearly the input is not in key value format, so here record reader is used to read input file and convert each line in key vaule pair. Here each line will be assigned a key by record reader and the vaule will be the actual line content.
Mapper logic: Just take the vaules, and split on space to find words and assign word as key and 1 as vaule.
Shuffle & Sort: Transfer all the key vaule pairs on to single machine (reduer). Sorting will happen on keys, for example output will be in format: (key, {vaule, vaule, …})
Reducer logic: Iterate over list of vaules in a key and sum it up.
Note:
- Number of mappers will be equal to number of data blocks.
- Number of reducer is set by developer default is 1 but we can set to 0 or any higher number.
- System take care of shuffle and sort operation.
- Record reader works on mapper machine.
- If number of reducers are 0 then shuffle and sort will not execute.
Optimization
-
More work on mappers: It will optimize the processing as all mappers are executed parellely. More on this below in combiner section.
-
Increase reducer: When we cannot put more work in the mapper then we can think of increasing reducer. Example: if all mappers take 1 min and reducer takes 4 min then we can consider increasing number of reducer in order to optimize the run time.
-
No reducer: Where no aggregation required, example: filtering.
Note:
- No shuffle and sort will be executed if reducer is not used.
- If we have more than one reducer then output of each mapper is divided in n partitions if n reducers are in cluster, partition 1 from each mapper goes to reducer 1 and so on. Hash function is used to route which key value goes to which partition. Hash function is consistent so as all same keys are in the same reducer.
Combiner
In some cases, when work is moved more on the mapper that means we can have some aggreation work on mapper. Like if we need max value of the key then that can be performed on mapper as well. And the aggregation which is done on mapper is done by combiner process, it is executed on mapper machines itself.
But avoid using in case where data can change when executing on one machine compared to multiple machine like avg.
Note: Combiner logic is same as reducer logic in this case for example: max, min, sum.
Flow of data
record reader -> mapper -> combiner -> partitioner -> shuffle & sort -> reducer

Comments